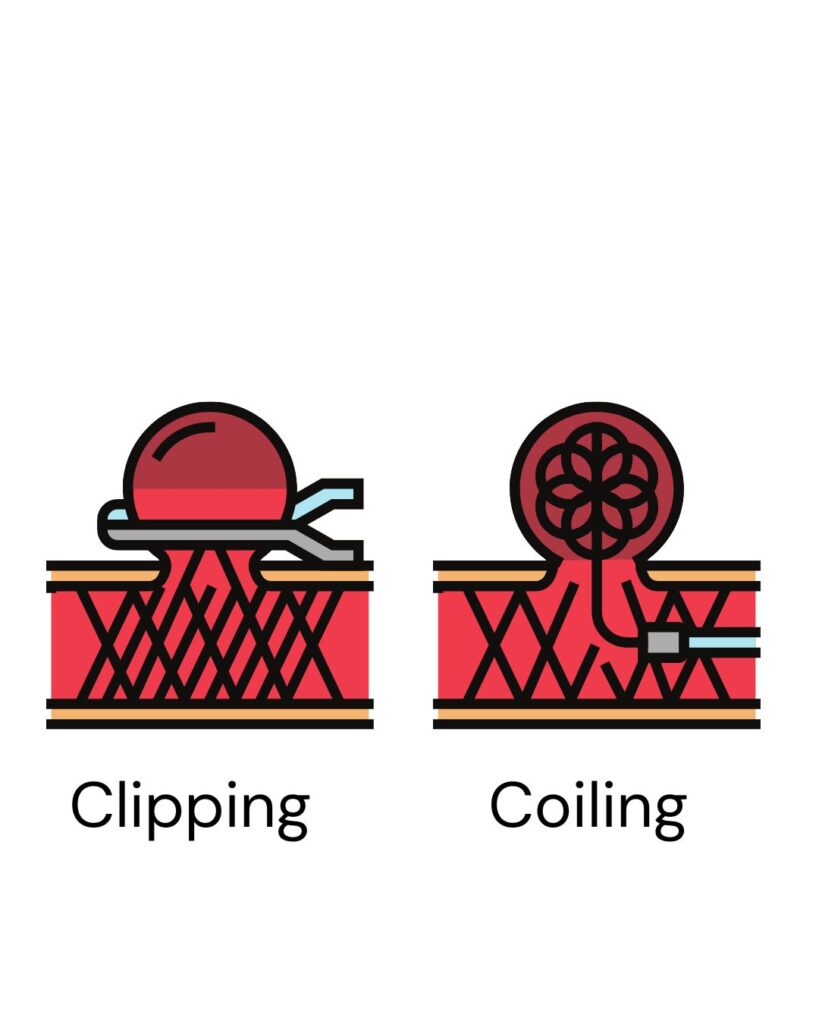
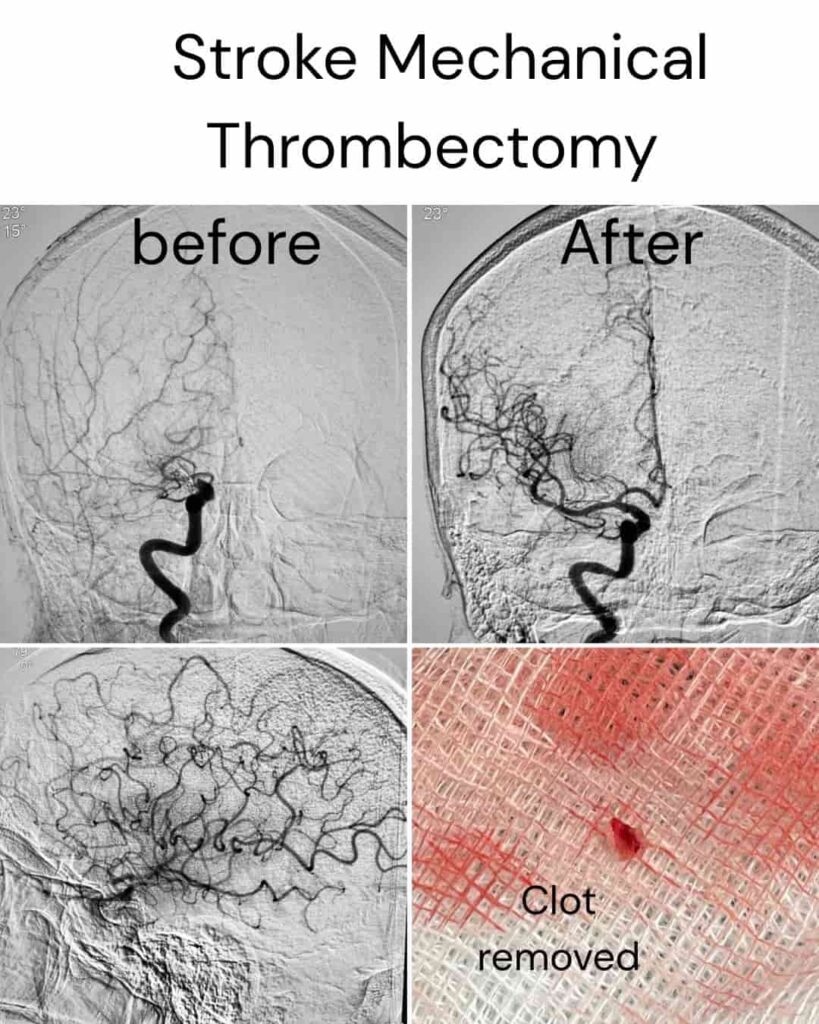
Causes
A brain aneurysm forms when a blood vessel wall in the brain weakens and bulges out like a balloon.
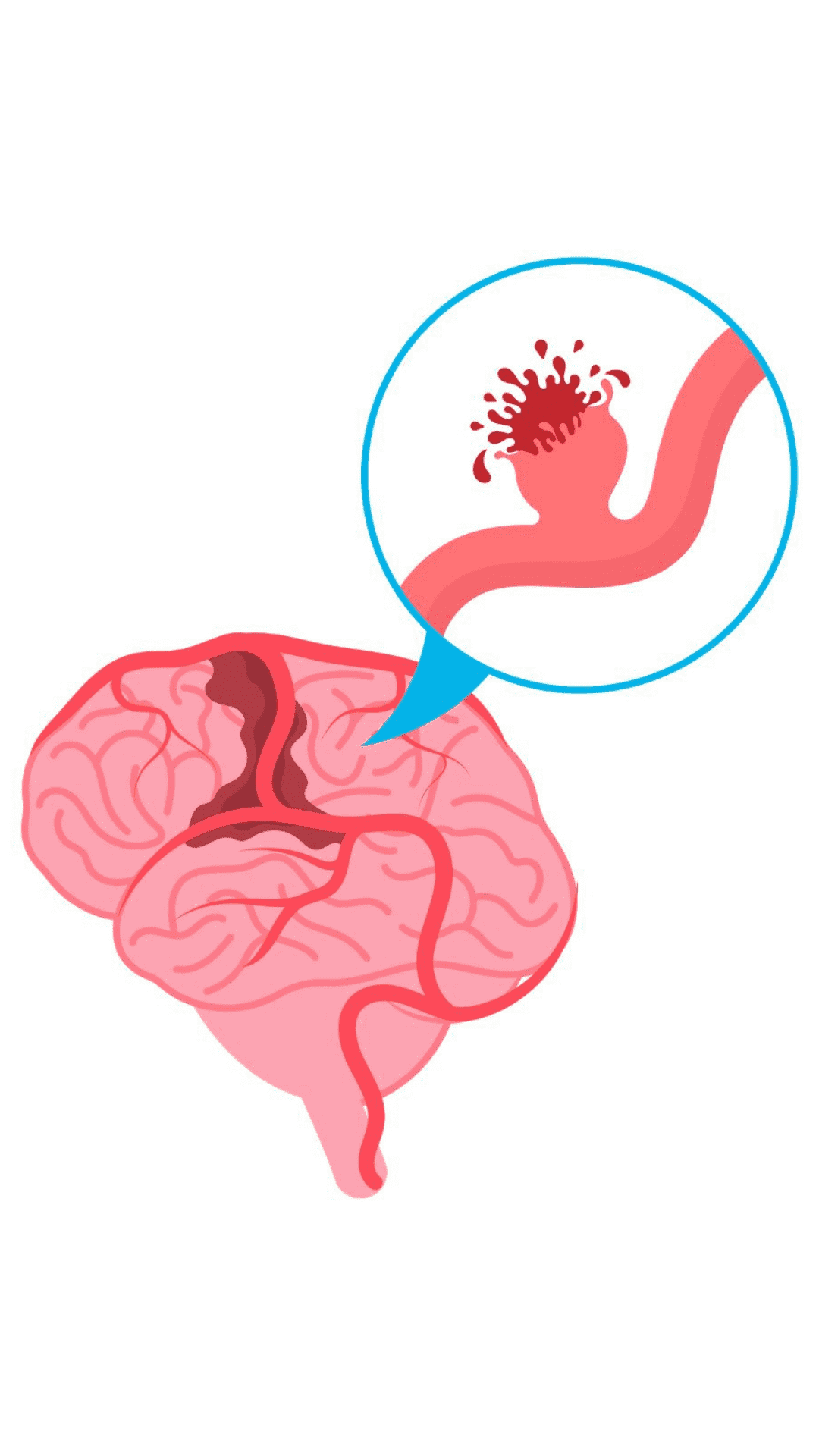
This weakness can develop due to several reasons:
- High Blood Pressure
- Family history of aneurysms
- Older age
- Smoking
- Head Injury